In today’s hyper-competitive retail landscape, retailers are increasingly using artificial intelligence to anticipate customer behavior, optimize internal operations, manage inventory levels, and create more strategic growth trajectories. AI is now found in many leading tools for retail, including data analytics platforms, CRM, ERP, and chatbots.
Enterprises that want to gain competitive advantage need to learn how AI is reshaping the retail world for customers, employees, and business leaders alike and establish a foundational knowledge of the pioneering AI tools enabling this dynamic technology in the retail sector.
KEY TAKEAWAYS
Retailers can benefit from AI across their business model through inventory and supply chain optimization, efficient sales and marketing content creation, smarter data analytics, and more personalized customer interactions. (Jump to Section)
Emerging generative AI tools for retail are particularly adept at handling hyper-personalized retail marketing tasks, including customer sentiment analysis. (Jump to Section)
Advanced technologies like computer vision, robotics, natural language processing, predictive analytics platforms, and AI copilots enable comprehensive retail AI platforms that can view the actions of and respond accordingly to e-commerce customers. (Jump to Section)
Major enterprises across industries are investing in AI primarily to improve their product listings, customer interactions, content creation verticals, and inventory management processes; smaller companies are beginning to follow suit. (Jump to Section)
TABLE OF CONTENTS
Understanding AI in Retail
Artificial intelligence in retail can take many forms depending upon what it is programmed to support. Consequently, AI adoption in retail depends on how and where business leaders choose to focus their AI efforts.
For most retail organizations, AI models are fine-tuned to act as standalone digital retail platforms or are embedded into existing retail platforms, ERP systems, AI CRM software, and business websites. These models are trained to handle a variety of behind-the-scenes and customer-facing tasks, including helping to manage inventory, supply chain processes, customer interactions, data analytics, and other features of the retail lifecycle.
Comprehensive retail AI deployments can view, absorb, and make future adjustments based on every customer interaction, click, and movement of inventory, looking at each of these steps in the retail lifecycle as a unique data point. Often, this data is absorbed into the AI model’s training set and used to further specialize and fine-tune the model’s ability to interact with customers. The model grows iteratively to deliver the personalized support and buying experience they want.
While many people fear that incorporating too much AI into retail will hurt business outcomes because of the loss of human touchpoints with customers, early adopters are finding the opposite to be true. AI can successfully mimic many human qualities in customer interactions, freeing up time for human employees to tackle more complex customer concerns and work on the strategies behind more user-centric customer experiences for the future.
5 Reasons Why Businesses Need AI in Retail
AI can improve retail operations in an ever-growing number of ways, including boosting customer engagement, improved marketing strategies and streamlined supply chains.
Enhanced Customer Experience
As shopping increasingly moves to an e-commerce format, retailers confront a difficult paradox: Customers are physically more distant yet expect a more personalized experience when shopping online. While hyper-personalization is difficult to achieve at scale for any retailer, AI software can ingest a vast number of data points and parameters and apply this information to create more personalized customer support, ads, product listings and other customer engagement strategies.
Supported by AI technology that is specifically designed with retailers and their customers in mind, ads are better targeted at what users actually want, chatbots can more clearly answer user questions on a customer’s schedule, and AI-driven apps give users access to new types of shopping experiences that fit their preferences. Although there may be less human-to-human contact in retail as AI is adopted, customers are on the receiving end of a customer-first experience that relies on intelligent algorithms to learn and adapt to their shopping behaviors.
Optimized Inventory Management
Artificial intelligence can automate conversational workflows, inventory and supply chain management, and other repetitive retail tasks that have traditionally required human touch. In inventory management, using AI reduces the chance for human error, ensuring inventory levels are neither too high nor too low and are proactively adjusted for predicted changes in demand. AI is already being used to support demand forecasting for highly specific retail seasons and shifts, as well as to automate stock replenishment.
As AI takes over customer service and inventory management touchpoints, retailers can reduce their staff or focus their attention on more strategic tasks. Especially as more and more of the workforce moves away from retail and service-based industries, these AI instances will help to fill in a production gap with limited retraining and recruitment requirements.
Improved Sales and Marketing Strategies
Sales and marketing strategies of yesteryear have sometimes felt like a shot in the dark, requiring retailers to make decisions based on limited data and visibility into customer behavior. With AI technologies in place, businesses can develop comprehensive buyer personas that take into account all buyer behaviors, more specific demographics, and multichannel interactions (including unstructured data from these channels).
Sales and marketing AI tools not only help users to better understand their customers, but can also help them to craft strategic content for these customers. For example, many marketing and sales tools now include generative AI elements to help businesses quickly craft blogs, ads, product descriptions, and other content that is well-suited to reach and engage the right audiences.
Advanced Data Analytics and Insights
AI-powered analytics tools democratize the analytics process with natural language inputs and outputs, contextualized explanations, and more detailed and accurate predictive analytics that are useful to marketing and sales teams. These tools can also analyze greater quantities and different types of data than most traditional marketing analytics tools can. A growing segment of AI data analytics tools also offer a prescriptive component, providing useful recommendations or even carrying out recommendations for improving operational workflows in a retail ecosystem.
Streamlined Supply Chain Operations
Advanced AI technologies like computer vision and robotics are designed to monitor the entire supply chain and inventory management lifecycle, identifying an error as soon as it occurs. This makes it easier to mitigate stocking and shipping errors before they lead to unhappy customers or inventory shortages. The level of detail and insight AI provides also helps businesses of all sizes to develop dynamic and just-in-time stocking methodologies, so they’re less likely to over-order or under-deliver in any of their markets.
Essential AI Tools and Technologies for Retailers
The number of AI technologies supporting retail operations is growing rapidly; some are still pioneering, like visual recognition, while others are well established but improving quickly, like AI-based chatbots.
AI-Powered Chatbots
AI chatbots with access to varying degrees of information can be embedded into customer-facing e-commerce sites, social media, and other applications. Going a step beyond chatbots that rely on a few manual workflows for specific conversational topics, AI chatbots are trained on a variety of subjects—often including an organizational database. This allows them to more effectively understand and respond to diverse customer questions and requests. With algorithmic training on such large sets of historical data, AI chatbots can handle much more complex customer questions and requests than previous chatbot iterations.
Some AI vendors don’t take over customer service interactions altogether but instead provide live coaching and suggestions to human customer service representatives. These live suggestions are often combined with detailed customer dashboards that give reps both the tools and the language they need to have a more product-focused conversation with customers on the phone.
Personalization and Recommendation Engines
Based on individual users’ metadata, past purchases, ad engagement, sentiment analysis and other data-driven inputs, retail AI solutions can now recommend products and services to customers that they may not have otherwise considered purchasing but are likely to want. Indeed, recommendation AI is one of the fastest-growing AI-retail areas because of how well it connects with and monetizes customer preferences.
Historically, human marketers and ad managers work behind the scenes to analyze how ads are performing and then decide what changes should be made to get more audience engagement. AI is quickly taking over this task on a widespread scale and making more accurate targeting decisions, primarily because these technologies are able to analyze a greater quantity of engagement data points more quickly.
Retail AI software also more frequently identifies subtle data patterns that humans may overlook. Additionally, these tools can make intelligent, fast-paced decisions based on past data, whether that’s updating ad copy based on user sentiment or changing where the ad falls on a webpage based on previous heatmap data.
As this technology continues to advance, AI is targeting hyper-personalized ads to individuals based on their metadata, prompting them to be more interested in and engage with advertising materials. Also significant, some AI models are monitoring, learning, and updating ads in real time, ensuring that ads are always optimized for the current audience.
Read our guide to the top 20 generative AI companies to learn how today’s generative AI leaders are serving businesses in a range of sectors.
Intelligent Analytics
AI-driven data analytics give users—including non-data scientists—a better understanding of all the different kinds of data at their disposal. These models can analyze data in different formats and in large quantities, looking at historical and current purchasing metadata across different categories to more accurately forecast demand.
For example, business owners may use AI analytics to learn that the sweaters they sold last year not only sold quickly but were reviewed favorably in customer reviews and conversations. They may also learn that while the sweater sold well in the Midwest, Northeast, and most of Europe, it did not perform as well in other U.S. regions or most of Asia. Armed with this data, the retailer will know that it should bring back this product but that some markets require more stock while others require less.
For the non-data scientist, AI analytics tools are particularly effective at offering prescriptive analytics, or analytics that make recommendations for how to adjust business tactics in the future based on current data. The natural-language approach these AI tools can take helps business users across departments and areas of expertise deploy this data for better results.
Automated Inventory Management Systems
AI-supported demand forecasting is one of the ways retailers are now more accurately predicting how much inventory they need and where and when it should be stocked. AI-driven data analytics may also help retailers determine when prices should be changed, how seasonal purchases impact inventory levels and supply chain movement, and where customer returns require more frequent inventory shifts.
In a more tangible sense, AI-driven robotics and computer vision can be used to support automated inventory management, whether that’s through just-in-time restocking or dynamic safety stock management. A growing number of retail warehouses are relying on AI assistive robots to scan inventory and monitor stock levels and then restock or remove stock as needed.
Visual Recognition and Security Enhancements
Through a combination of biometrics and AI recognition technology, storefronts are starting to simplify the user checkout experience, including in physical stores. For example, some stores are now allowing repeat customers to simply grab their items and walk out the door; the store’s AI recognition and scanning technology recognizes the customer and automatically charges them without requiring them to physically check out.
This same system’s reliance on biometric technology may also help retailers more quickly identify and solve problems when it comes to shoplifters. For customers that want a more user-friendly e-commerce shopping experience, many companies have added AI assistive elements to their retail apps. These features may make purchase suggestions or integrate with virtual wallets for a smoother shopping experience.

AI Copilots
AI copilots are essentially virtual assistant AI models that have been trained to support business leaders and employees with their day-to-day tasks. In retail, AI copilots may be tasked with providing real-time updates on sales and performance analytics or producing new product descriptions or listings. They also give in-store employees up-to-date information about store policies and inventory availability, and equip managers with information about employees’ schedules and staffing gaps.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning algorithms are trained to recognize and act on the differences between different users and data points, including ad clicks, purchases, and customer service conversations. This type of AI is particularly useful for making predictions about overall brand sentiment, what users most want to purchase, and how purchase trends will change over time.
Natural Language Processing
Generative AI is well-suited for building chatbots, virtual assistants, and other AIs that help customers directly by generating content in response to their queries. This is possible because of the natural language processing (NLP) and natural language understanding (NLU) that are inherent to generative AI and large language models. With their deep training in and understanding of human language and communication, as well as data stored from previous interactions, generative AI models can directly answer customer questions and even make purchase suggestions based on a customers’ past purchases or preferences.
Computer Vision Systems
Computer vision is a type of artificial intelligence technology that has been trained to see and respond to its physical environment based on visual triggers. Retail greatly benefits from this type of AI, as computer vision supports cashierless checkout infrastructure and other personalized shopping experiences that require fewer human interactions to run smoothly. Behind the scenes, computer vision may also be used to monitor and manage inventory levels, analyze customer behaviors in physical storefronts, and better detect and mitigate suspicious shopper activities in stores.
Robotics and Automation
AI-powered robotics is a fast-growing subfield of retail AI that can power physical machines that move inventory or provide a useful shopping interface for customers onsite. Robotics and automation workflows may be used to scan, update, or shift inventory from warehouse to storefront; drive delivery vehicles and drones; or physically interact with or provide a checkout mechanism for customers in stores.
Predictive Analytics Platforms
Predictive analytics platforms combine AI, statistical data modeling, and massive historical datasets to create accurate predictions for retail metrics related to future purchases and buyer behaviors. Some of these tools also rely on third-party datasets, internet connectivity, and APIs to assess competitor performance and decisions and determine how these might impact retailer pricing and stocking decisions.
With a predictive analytics platform that is supported by AI, the AI component can quickly give users natural language insights into where sales, marketing, and operational decisions are working and where they could use adjustments. Hyper-personalized advertising and product listings, targeted loyalty programs, and price changes are all examples of retail shifts that may be informed by demand forecasting and other data provided by a predictive analytics tool.
Ways to Drive Your Retail Marketing With AI
Traditional marketing technologies lack the detailed insights and extensive support that AI can provide. Here are some of the ways AI can support a far more effective marketing strategy for retail businesses:
- Targeted Advertising and Promotions: AI can analyze past customer purchases and clicks, heatmaps, and granular customer demographic information that may not be noticeable to humans who are less familiar with demographic data. From there, AI can be used to develop targeted ad content and send it to the right people at the right time.
- Customer Segmentation and Insights: Unlike traditional customer segmentation based on broader demographics or purchasing history, AI-driven customer segmentation can use highly specific data to create more targeted, purchase-ready segments of buyers. Within these segments, AI can also be used to uncover even more insights and information that may inform how you develop ads—or even new products—that cater to this group of buyers.
- Personalized Shopping Experiences: By recording and analyzing responses to a suggestion on a product page, AI quickly identifies likely buyers and predicts what they will add to their cart based on their behaviors and purchasing history. These suggestions are provided in a way that does not disrupt the shopping process—in fact, many customers appreciate being targeted with products they may not have known about but can benefit from.
- Dynamic Pricing Strategies: In real time, AI technology can assess product demand, competitor prices, customer sentiment, and other factors to determine if products should be repriced in that moment. Dynamic pricing often leads to higher sales numbers without requiring retailers to take hands-on action.
- Social Media and Sentiment Analysis: AI models can collect and analyze multichannel customer feedback to give retailers a better understanding of how customers feel about the brand and specific products. Particularly with large language models and generative AI models, unstructured data like text can be collected from multiple different sources, and at the same time, spammy reviews can be filtered out so they don’t muddy the waters of your analysis. Retailers can apply these new sentiment insights to more personalized customer experiences, including catered ads and more precise audience segmentation.
3 AI Tools for Retailers You Should Consider
Given the advantages offered by AI retail tools, it’s imperative that retailers employ an array of AI applications to boost sales and streamline business processes.
ai.RETAIL: Better Insight Into Data
Accenture, the global professional services firm, is the mastermind behind ai.RETAIL, an AI and data analytics platform that helps retailers better understand their data both at an individual customer and big picture level. Its features include customizable customer-level views that show historical buying patterns and loyalty, dynamic merchandising for different customer channels, supply network digital twin development, and customer targeting capabilities.
For example, Canada-based restaurant chain Tim Hortons has used ai.RETAIL and other products and services from Accenture to set up its customer loyalty app. This app includes personalized rewards and intelligent data analytics that help the vendor to keep customers engaged with the brand.
Stackline Shopper OS: CRM for Retailers
Stackline’s Shopper OS is a back-end platform for retailers that allows them to manage different aspects of customer relationships with the help of AI, going beyond the traditional CRM. Its main features include a multi-retailer CRM, syndicated ratings and reviews, reward and loyalty program development, AI-targeted surveys and automated customer messaging. It also offers an AI-driven analytics tool that looks at shopper behaviors across different retailers, channels, and platforms.
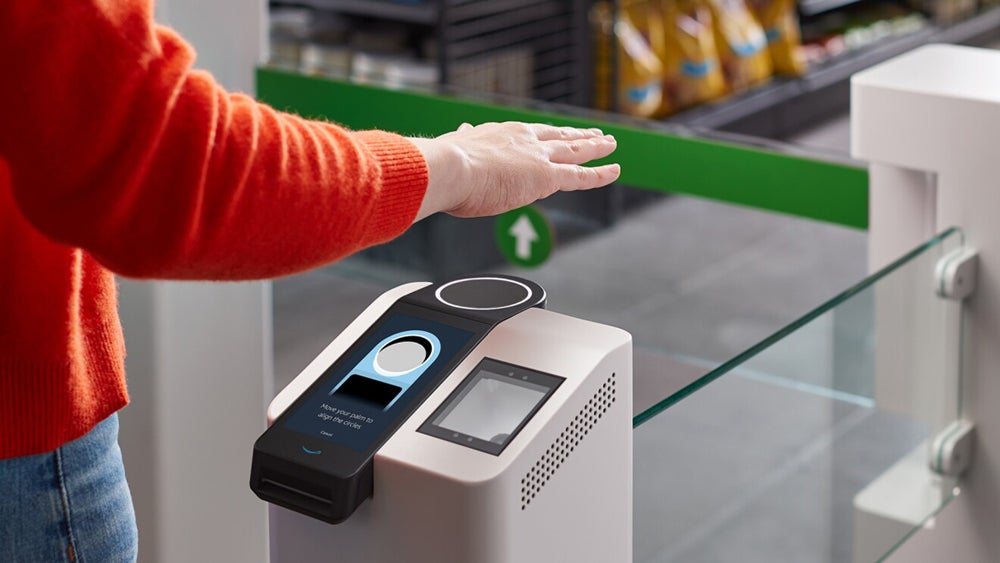
Amazon One: Streamlined Shopping
Amazon One is an AI-driven solution that Amazon has built to simplify the customer-side of each retail interaction with a shopping experience it calls “Just Walk Out” shopping. With Amazon One, a customer’s payment information is linked to their palm, and AI and machine learning are used to identify that palm and charge the appropriate person’s account when they leave a participating store with a purchase. This means users can quickly pick out their items and leave without going through a traditional checkout process.
Read our guide to the top AI retail solutions transforming the industry to learn more about the vendors and products having the biggest impact on businesses.
Case Studies: How Leading Brands Use AI in Retail
Leading players, from e-commerce to traditional in-store retailers, have already invested heavily in AI solutions to boost sales. In fact, many of the solutions these giants use are used across several industries.
Amazon: AI in E-Commerce
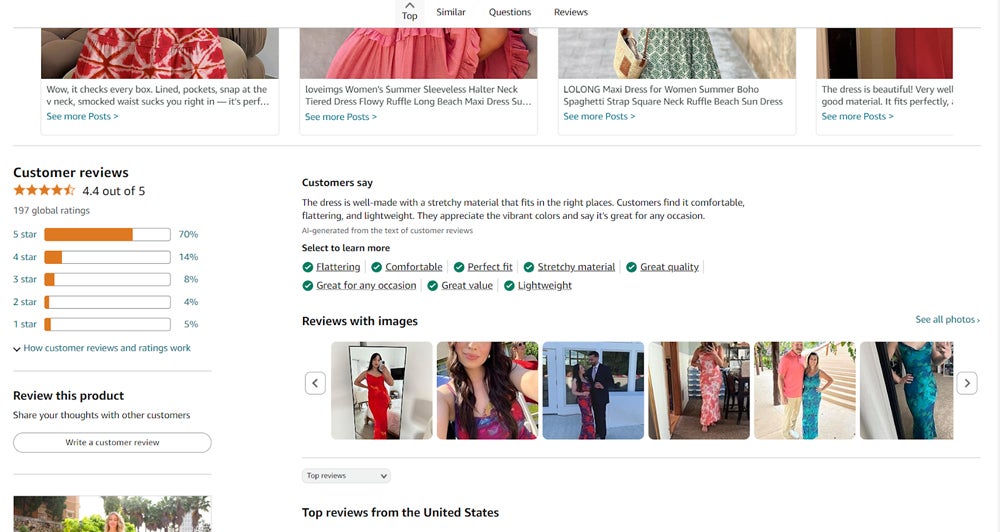
As a longtime pioneer of AI and machine learning solutions, developing tools both internally and for its vast network of partners and clients, Amazon has infused AI into its operations at various levels and for a range of purposes. A recent example of how it has used AI to improve customer experience is the “customers say” feature added to Amazon customer reviews. This AI-generated content is effectively a summary of all reviews provided on any given product, giving customers a quick-glance opportunity to learn what customers do and don’t like about the product they’re thinking about buying.
Walmart: AI in Traditional Retailing
Walmart has leaned heavily into conversational AI in recent months, especially as many of its customers have begun to engage with the brand online. With Walmart Voice order and Text to Shop, users can purchase and repurchase different items through their mobile devices without going through the actual motions of making the purchase. Walmart’s AI recognizes the buyer and their past purchases and payment methods to make the purchase on their behalf.
Additionally, Walmart has improved both its internal and customer-facing chat interfaces. Its customer support chatbots are now supported by AI, enabling chatbots to handle most customer queries and requests, while only the most complicated conversations are handed off to human support representatives. Internally, Ask Sam is a voice assistant that helps in-store associates whenever they have questions about their schedules, their coworkers, and other important workplace information.
Kroger: AI in Grocery and Food Retailing
Kroger has begun working with Intelligence Node, an AI retail intelligence company, to optimize its product pages and taxonomy so the information customers want about different products is easier to find, more detailed, and more up-to-date. This work may include improving rankings on search result pages, generating new and more effective product descriptions, and providing more detailed analytics data for how product pages are performing.
Zara: AI in Fashion and Apparel
Zara is an international fashion brand that is using AI technology to manage supply chain, inventory, and customer return workflows in particular. It uses a process called Just-In-telligent supply chain system management, which combines AI-driven inventory management and data analytics to improve real-time supply chain updates. The brand has also worked with Jetlore (now owned by PayPal), a predictive retail AI company, to help Zara better predict customer behaviors and purchasing decisions based on more granular clothing data points. The company reported that using AI in these ways has improved its deliveries, inventory carrying costs, and issues with returns.
Bottom Line: Retailers Embrace AI for a Competitive Edge
Retailers are getting creative and finding all kinds of ways to incorporate AI to gain a competitive advantage. This ranges from allowing AI to directly interact with or indirectly influence customer interactions, restock and monitor inventory across distributed sites, or give business leaders a more detailed view of current performance data. As retailers implement AI strategically, it can benefit both employees and customers with automation, personalization, and hands-off features that improve the overall retail experience.
See our guide to the top generative AI tools and applications to explore the most popular solutions in this dynamic and emerging technology on the market today.