KEY TAKEAWAYS
- •Collaboration between humans and AI boosts productivity by combining human intelligence with AI’s ability to process data and automate tasks. Together, they’re helping industries work faster, solve problems, and spark new ideas. (Jump to Section)
- •Despite its progress, AI has limits — including data bias, a lack of common sense, and trouble understanding context. These issues can lead to hallucinations. It also demands heavy computing power, and raises ethical concerns that slow adoption. (Jump to Section)
- •
- Emerging AI trends include multimodal AI, which understands different types of input; agentic AI, which focuses on Autonomous systems; and retrieval-augmentation (RAG), which combines AI content with real-time information. (Jump to Section)
Artificial intelligence (AI) involves using algorithms, large datasets, and computational power to enable machines to perform tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include recognizing patterns, understanding language, and making decisions.
Unlike natural intelligence, which arises biologically in humans and other animals, artificial intelligence is a human-created system. It is designed to replicate specific aspects of intelligent behavior through computational needs.
Early AI pioneer John McCarthy coined the term “AI” to describe the field of creating intelligent systems. These systems are capable of executing tasks that traditionally require human intelligence — such as decision-making, problem-solving, and understanding language.
AI has evolved to handle such complex tasks as identifying patterns in data and generating creative content. As a result, it has become an important tool across various industries.
Here’s what you need to know about this dynamic technology: how it works, how it’s being used across industries, and how to implement it into your own workflows and business.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
What is AI in simple terms?
AI allows computers to do tasks that used to require human intelligence. These include understanding and generating language, recognizing images, creating art, and learning from past experiences.
AI systems can study data, get better over time, and even predict future outcomes. They do this using techniques like machine learning (ML) and neural networks.
These systems are built to imitate how people think. That means they can talk to humans in natural language, solve complex problems, and even come up with creative ideas.
Although AI is still improving and getting more complex, it is already generally available. Everyday users can employ AI tools for a variety of tasks, including writing, image generation, data analysis, and decision-making, expanding the possibilities for personal and professional applications.
Types of AI
Experts classify AI in different ways. The two most common categories are narrow AI and general AI. Narrow AI is built for specific tasks. General AI is designed to do anything a human can do.
Here are the most common types:
- Artificial narrow intelligence (ANI): Designed to complete one task or set of tasks with high competence and skill. Apple’s Siri, IBM’s Watson, and Google’s AlphaGo are all examples of Narrow AI.
- Artificial general intelligence (AGI): Can handle many intellectual tasks at a human level. Many researchers are currently working on developing general AI.
- Artificial superintelligence (ASI): Is still theoretical, has intellectual capacities that far outstrip those of humans but is not yet close to becoming a reality.
How AI works
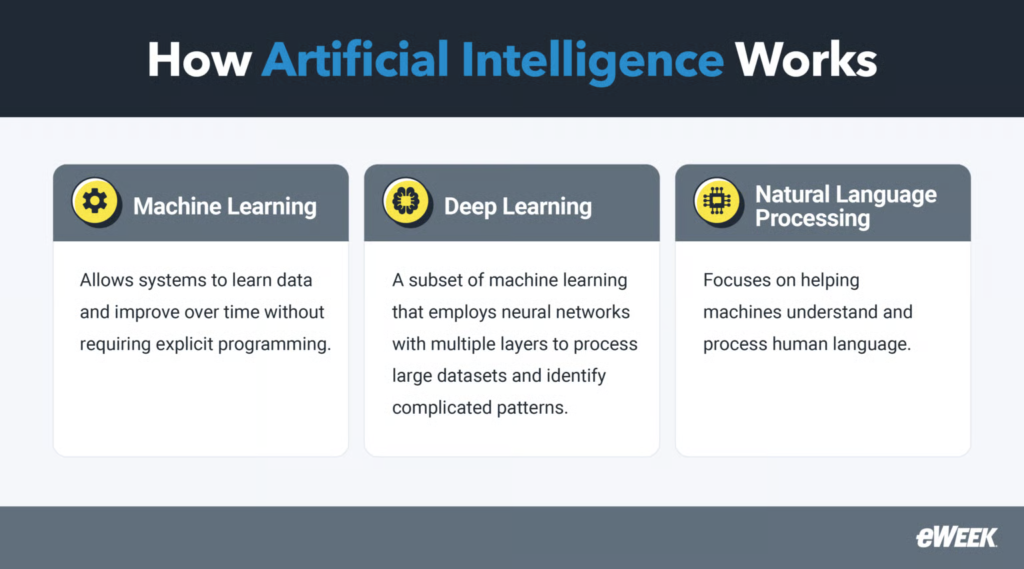
AI works by using different algorithms and training data to identify patterns and make predictions or decisions. It often does this without needing explicit instructions for every possible outcome.
The field of AI is broad. It includes machine learning, which helps systems learn from data. It also includes deep learning, which uses neural networks to recognize complex patterns; and natural language processing, which focuses on interpreting human language. Together, these technologies drive progress in various industries, including healthcare, finance, and entertainment.
Machine learning
ML allows systems to learn data and improve over time. It doesn’t require step-by-step programming for every task.
Models generally fall into three types:
- Supervised learning: Uses labeled data to train models.
- Unsupervised learning: Finds hidden patterns without labels.
- Reinforcement learning: Learns through feedback from their environment, using rewards or penalties to guide actions.
Building and training ML models typically involves using specialized frameworks such as TensorFlow or PyTorch, which provide tools for defining, optimizing, and deploying models.
Deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of ML that uses neural networks with multiple layers to process large datasets and identify complicated patterns.
These neural network architectures are commonly used in deep learning:
- Neural network layers: Include input, hidden, and output layers that work together to process information.
- Deep neural networks (DNNs): Standard multilayer neural networks that learn advanced features through multiple hidden layers.
- Convolutional neural networks (CNNs): Specialized for image and video processing.
- Recurrent neural networks (RNNs): Ideal for handling sequential data like text, speech, or time series.
Natural language processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a field of AI focused on helping machines understand and process human language.
Key NLP techniques used to process and analyze text:
- Tokenization: Breaks down text into smaller units like words or phrases.
- Part-of-speech tagging: Labels each word with its grammatical role.
- Named entity recognition (NER): Identifies proper names such as people, places, or organizations.
- Sentiment analysis: Determines the emotional tone expressed in the text.
Popular NLP models trained to understand and generate language:
- GPT (Generative Pretrained Transformer): Predicts and produces text, powering tools like chatbots and writing assistants.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): Excels at understanding word context in sentences, improving tasks like search and translation.
Real-world use cases of AI
AI powers many practical applications such as language translation, data analysis, recommendation systems, and more. The possible AI use cases and applications for artificial intelligence are nearly limitless. Here are some of the most common AI use cases:
- Virtual assistants: AI-powered virtual assistants such as Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant use NLP to recognize spoken requests. They can handle tasks like setting reminders, managing smart devices, and answering questions.
- Content generation: Generative AI models are being used to generate content in a variety of formats — including text, code, synthetic data, audio and music, images, video, and voice.
- Recommendation engines: Recommendation engines use ML models to compare your selections and historical behavior to those of others. They then suggest products or services you might like and often spot preferences you didn’t even know you had.
- Sentiment analysis: This helps customer support teams identify people who may be unhappy or those who are enthusiastic and might become brand advocates. AI can analyze language and detect the emotions behind conversations.
- Voice synthesis and assistance: This involves advanced AI techniques, including NLP and machine learning. It can be used on smartphones, smart speakers, laptops, and even self-driving cars.
- Fraud prevention: Banks and retailers use advanced machine learning to detect fraudulent transactions. They analyze financial data and flag anything unusual or that matches known fraud patterns.
- Image recognition: AI looks at visual data to find patterns and make decisions. For example, doctors spot problems in medical scans early, leading to better treatment. Facial recognition is also used in security and retail to offer personalized product suggestions.
- Predictive and prescriptive analytics: Predictive algorithms can analyze just about any kind of business data to forecast future events. Prescriptive analytics goes further by suggesting actions a company should take in response. While still developing, this approach is growing fast.
- Autonomous vehicles: Many cars today already have some autonomous features, like parking help, lane centering, and adaptive cruise control. Fully autonomous vehicles are already on the road, and the AI technology that powers them keeps getting better and cheaper.
- Robotics: AI-powered robots are changing the way businesses work. They handle repetitive tasks, assist in surgeries, and support patient care. These robots improve precision, reduce errors, and boost efficiency.
- AIOps: Artificial intelligence for IT operations (AIOps) uses AI to automate and improve how IT systems run. It can predict system issues, optimize resources, and quickly identify problems by analyzing massive amounts of data. This helps businesses stay efficient, avoid downtime, and keep systems reliable.
Advantages of AI
AI provides benefits across sectors, resulting in considerable increases in efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making processes. Some of the main benefits of AI include improved accuracy, higher efficiency, and task automation, which helps free up employees’ time.
High levels of accuracy
AI systems are excellent at completing tasks with high accuracy. For example, ML algorithms can scan large datasets, detect trends, and make accurate predictions. This decreases human errors in tasks like data entry, calculations, and even diagnosing medical issues.
Using AI in areas like healthcare, banking, and manufacturing leads to more consistent results and better overall performance.
Increased employee availability
By automating repetitive and time-consuming tasks, AI allows staff to spend more time on significant and complicated work. AI-powered solutions, such as chatbots, can handle admin tasks, scheduling, and customer service. This frees up human workers to focus on strategy and creative problem-solving. As a result, employees can take on more meaningful work, leading to greater productivity and job satisfaction.
Advanced content generation capabilities
AI technologies such as NLP and ML have made it possible to generate high-quality content and analyze data on a large scale while being cost-effective to end users. GPT-4, for example, can produce articles, marketing material, and even technical writing in a human-like tone. In addition, AI-powered data analysis tools can swiftly filter through massive datasets, yielding insights that people might require days or weeks to unearth.
This ability helps companies respond faster to changes in the market and customer needs.
New research and discoveries powered by AI-driven analysis
AI is changing the way research is done by speeding up discoveries in different fields. In healthcare, AI helps analyze genetic data, discover new drugs, and predict patient outcomes.
In the pharmaceutical field, AI models speed up the drug development process, saving both time and money.
AI’s ability to process complex data uncovers new patterns that traditional methods could not detect. This leads to innovations that were once thought impossible.
Challenges and limitations of AI
While artificial intelligence provides significant benefits, it also comes with challenges and limitations. From high operating expenses to ethical considerations, it’s important to recognize these issues to ensure proper and responsible use.
Bias and ethics
AI models are only as good as the data on which they are trained; if the data is biased, the AI will likely reflect those biases. For example, facial recognition technology is known to make mistakes — particularly when identifying people of color — because of biased training data.
Ethical issues occur when AI systems are used to make decisions in areas like hiring, lending, or law enforcement based on flawed or incomplete data, which can lead to unfair outcomes. To address these, AI should be trained on diverse, representative datasets, and its decision-making procedures should remain transparent.
Beyond technical bias, humans must also have conversations about AI’s broader impact on society, including privacy, accountability, and human rights. Creating ethical AI means not only reducing bias but also protecting people and upholding their freedoms.
Security risks
AI systems, particularly those that handle personal data, are prime targets for cyberattacks.
Hackers commonly use flaws in AI systems to steal sensitive data, tamper with AI-generated outputs, or disrupt essential services. Adversarial attacks, where attackers feed AI misleading data to cause errors, are a unique threat. For instance, a bad actor could manipulate AI systems used in self-driving cars or financial platforms, with potentially dangerous consequences.
Cost and resource usage
Another major challenge with AI is its cost and energy use. Training sophisticated AI models, particularly deep learning models, requires massive compute power that rely on sophisticated technology (like GPUs) and power-hungry data centers.
As a result, smaller enterprises and organizations may find it too expensive to build, manage, and operate AI systems. As AI use grows, the environmental impact of energy-intensive data centers is an increasing concern.
Industries using AI
AI has become a powerful tool across numerous industries, transforming business operations and the way services are delivered. Below are some key sectors where AI is making a significant impact.
Healthcare and medicine
AI is revolutionizing healthcare by improving diagnoses, treatments, and patient outcomes. In medical imaging, AI systems analyze X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans to detect ailments and conditions like cancer or fractures more quickly and accurately than traditional methods.
AI-powered tools also help predict patient outcomes and create personalized treatment plans, improving the quality of care.
The same applies to drug discovery, where AI helps identify new treatments faster, cutting down the time and cost needed to bring drugs to market.
Finance and banking
In the financial industry, AI is used to detect fraud, assess risk, and automate repetitive tasks. For example, ML models can scan financial data in real-time to identify unusual patterns that may indicate fraudulent activities. Banks also use AI to evaluate credit risk. It does this by analyzing a customer’s financial behavior and history, which leads to more accurate lending decisions.
AI is also being used to improve customer experience in the financial industry. This includes deploying chatbots and creating more personalized services. But personalization is not just about chatbots. It also shapes how banks market their products. By analyzing customer behavior, AI gives marketing teams helpful insights that allow them to tailor products and services to match what customers want and need.
Education and learning
AI improves education by customizing learning and automating admin work. AI-powered platforms can adjust lessons based on a student’s progress, skills, and limitations. This results in a learning experience that adapts in real time.
AI is also used to develop intelligent tutoring systems, which give students one-on-one help outside the classroom. It also helps with grading assignments and managing student records. This gives teachers more time to focus on meaningful interactions with students. In addition, AI supports content creation by generating quizzes, lesson plans, and learning materials based on curriculum needs.
Transportation and logistics
AI is changing transportation and logistics by optimizing routes, increasing safety, and allowing self-driving trucks. In logistics, AI algorithms evaluate data like traffic patterns and weather to find the best delivery routes, resulting in lowered costs and delivery times. AI is also useful in fleet management since it helps companies estimate maintenance needs and reduce vehicle downtime.
Autonomous cars powered by AI are advancing in both personal and commercial use. These self-driving technologies use sensors and cameras to safely move through traffic. AI also improves driving aid systems, such as autonomous braking and lane-keeping devices.
Emerging trends in AI
As AI evolves, several new trends are shaping the future of the technology. These trends show how AI is growing in power, while also raising more ethical and security concerns.
The rise of multimodal AI
Multimodal AI refers to systems that process different data types, including text, images, audio, and video. This makes it possible for AI to understand and create content in more complex ways. For example, a multimodal system could describe an image or create a picture from a voice command. By combining different processing methods, these systems achieve higher performance.
Autonomous agents in more fields
Agentic AI is built to act independently, performing tasks, making decisions, and interacting with its environments without human intervention. It focuses on goal-oriented behavior and adaptive decision-making based on advanced algorithms and sensory inputs so it can perform real-time actions. It is now used in robotics, autonomous vehicles, and AI virtual assistants that work without constant human control.
Improved retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)
Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) is a method that improves generative AI models by allowing it to pull in outside information. With RAG, more accurate and appropriate responses. It combines the strengths of content generation and data retrieval, which raises the quality of AI outputs.
Rising demand for AI-skilled workforces
As AI continues to grow, so does the need for people who understand it. This includes data scientists, AI engineers, and machine learning specialists. Companies are investing in training programs to build teams that can use AI effectively in their operations.
Increased use of shadow AI
Shadow AI happens when people in a company use AI tools without IT’s approval or oversight. This can lead to problems with security, data privacy, and regulatory compliance. To reduce these risks, companies need to track and control the use of AI tools.
More scrutiny on ethics and security
AI is now used in many parts of society. As a result, it raises more concerns about its ethical use and security risks. These include bias in AI algorithms, misuse in creating deepfakes, and false data use during training. Organizations must have strong security measures to protect AI systems from being abused or attacked.
3 AI tools to try
Various AI tools are readily available for anyone to try, with the most popular being ChatGPT for text-based and image generative AI, Leonardo.AI for image creation, and GitHub Copilot for coding assistance. These tools are helping speed up the creative process for many professionals and even help non-content creators or beginner developers generate the specific outputs they need in their respective industries.
ChatGPT

ChatGPT, which stands for Generative Pre-trained Transformer, is OpenAI’s chatbot that uses advanced NLP to engage in conversations that closely resemble human dialogue. It can generate different types of text-based content, such as articles and poems. The free version answers questions based on its October 2023 knowledge cutoff and allows limited image generation with DALL-E. However, it lacks access to the latest models and advanced features.
ChatGPT Plus, priced at $20 per month, offers extended messaging, file uploads, data analysis, and higher image generation limits. It also includes access to multiple reasoning models like OpenAI o3 and o4-mini. Additionally, Plus users get early access to GPT-4.5 and GPT-4, create projects and custom GPTs, and test new features.
Leonardo.AI

Leonardo AI is a generative AI platform that specializes in image creation using detailed text input or prompts. It can generate different types of images, such as cartoons, hyper-realistic images, anime-related images that can be used for various use cases — web publishing, video games, and more. Leonardo has a free version that gives users 150 tokens daily to spend on creating their AI-generated images.
The amount of tokens required for image generation depends on the users’ image preset, but it usually starts at four tokens for default images and up to 26 tokens for images created using the Alchemy feature. For more tokens, Leonardo offers a monthly subscription. The Apprentice plan starts at $10 for 8,500 tokens monthly, the Artisan plan starts at $24 per month for 25,000 tokens, and the Maestro plan starts at $48 per month for 60,000 tokens.
GitHub Copilot

GitHub Copilot is an AI-powered coding assistant that helps generate and correct code for software developers. It integrates with integrated development environments (IDEs) and provides real-time code suggestions, autocompletion, and code generation based on NLP prompts. Developers can use it to simplify coding tasks and automate complex operations for different programming languages.
While AI accelerates development, users should review AI-generated code for accuracy, security, and legal compliance. Copilot offers a free version that gives users 500 MBs of private repositories. For more private repository spaces, Copilot offers 2GBs of repository space in its Team Plan, which costs $4 per month per user. The Enterprise plan provides 50GBs of repository space at $21 per user, per month.
3 beginner-friendly AI courses to learn more
If you’re exploring AI, taking online courses is a great way to get started or deepen your understanding. Several education platforms offer a variety of training programs — here are three beginner-friendly courses available on Coursera, included with a $49 monthly subscription.
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence (AI)
IBM offers an Introduction to Artificial Intelligence course ideal for beginners who want to learn more about AI, how it works, and how AI applications can be used. It also explains the potential issues, concerns, and ethical considerations that students need to learn when implementing AI into their lives.
Introduction to Generative AI
Google’s Introduction to Generative AI course teaches you about different generative AI model types. In addition, you’ll get to learn about different Google Tools to help you develop your own generative AI apps. This course is part of the Introduction to Generative AI Learning Path Specialization.
When you enroll, you’ll also be enrolled in this Specialization while learning new concepts from industry experts, gaining a foundational understanding of the subjects and tools, and developing job-relevant skills with hands-on projects.
Learn to code with AI
Interactive code-learning platform Scrimba offers this beginner-friendly Learn to Code with AI course to teach students how to use AI to build web applications — the only requirement is a fundamental understanding of HTML, CSS, and Javascript. You’ll gain skills in ML and computer programming and learn how to deploy web applications.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Simply put, AI refers to machines or software that can perform tasks that require human intelligence, such as speech recognition, decision-making, language translation, and even playing games. It can also be described as a digital assistant that learns from data and improves over time.
You can learn AI without coding using various no-code AI platforms that allow users to create and deploy AI models using visual, user-friendly interfaces. Tools like Google’s Teachable Machine, DataRobot, and MakeAI make AI accessible to beginners by allowing them to experiment with AI and ML, without needing to know any programming languages.
Learning AI from scratch can be challenging since it requires knowledge of several fields such as computer science, mathematics, and statistics — which may seem be overwhelming. On the other hand, today’s no-code AI platforms make it easier for beginners to learn AI. If you’re new to AI, start by researching the basics and enrolling in online courses. Many platforms offer free courses and tools that help you learn AI in an accessible and achievable way.
Bottom line: Use our artificial intelligence guide to navigate technology’s future
AI is already reshaping a wide range of industries, but the future brings both opportunities and challenges. As technology continues to evolve — with breakthroughs like quantum computing on the horizon — the real question is how society will respond to these innovations.
Whether it’s biased data or unmet financial expectations, businesses must navigate a range of challenges associated with implementing AI. This guide offers key insights to help you and your organization stay informed and ready for the future of AI technology.
Learn more about creating detailed and effective prompts through our Prompt Engineering Guide to unlock AI applications’ full potential.